Is itchy, irritated skin disrupting your life? Dermatitis may be the cause. This frustrating condition can cause various symptoms depending on the type, but effective treatments are available.
To learn more about the different types of dermatitis, their symptoms, and treatment options to find relief and improve your skin’s health, contact us directly or continue reading below.
Dermatitis is an umbrella term for a group of skin conditions that cause inflammation. It is characterized by itchy, dry, or irritated skin and can vary in severity and appearance. Several factors contribute to its development, including allergies, irritants, and genetic predisposition.
To effectively manage dermatitis, it’s essential to identify the specific type. Common types include:
Understanding the symptoms associated with each type is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
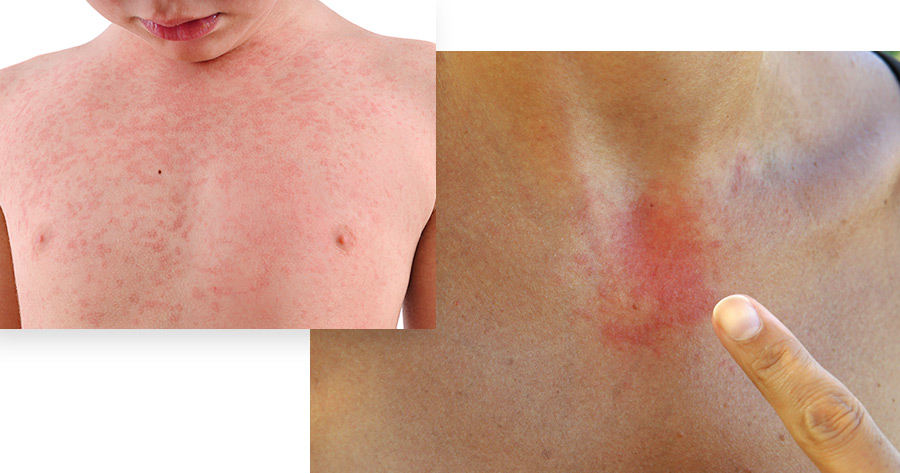
Dermatitis symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary significantly between individuals depending on the specific type of dermatitis. If you suspect you have dermatitis, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Dermatitis is often triggered by substances that irritate the skin. Everyone’s skin is different, so what bothers one person may not affect another. To effectively manage dermatitis, it’s essential to identify your triggers.
Common culprits include:
Avoiding these substances can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of dermatitis flare-ups.
Several factors increase your likelihood of developing dermatitis. Individuals with frequent exposure to harsh chemicals or metals are particularly susceptible. A family history of allergies or a personal history of allergies, asthma, HIV, or congestive heart failure can also elevate your risk.
The treatment for dermatitis depends on several factors, including the type of dermatitis, severity of symptoms, and individual patient needs. While over-the-counter products can relieve mild cases, more severe conditions may require prescription medications or specialized therapies.
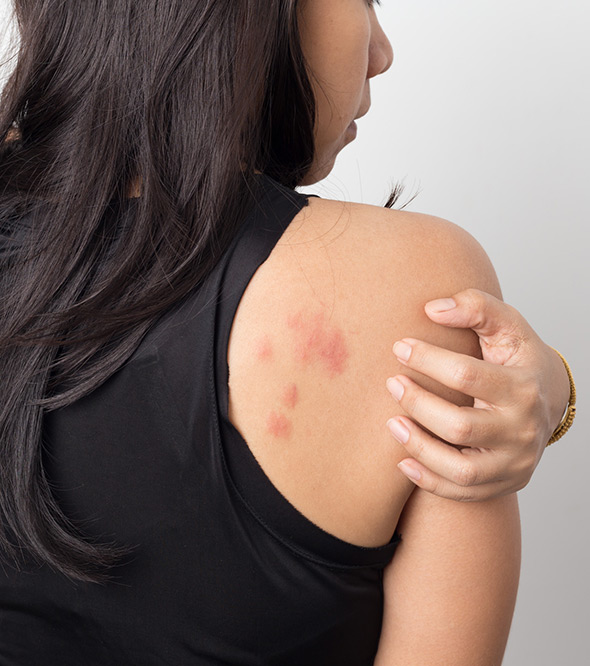

Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is a chronic condition that often requires ongoing management. Treatment typically focuses on:
The primary treatment for contact dermatitis is to avoid the allergen or irritant causing the reaction. Additional treatment options may include:
Treatments for seborrheic dermatitis aim to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
Perioral dermatitis can be challenging to treat. Common treatment approaches include:
The best way to manage dermatitis is to avoid triggers.
You can also help prevent flare-ups by keeping your skin hydrated, moisturized, clean, and protected. Choose fragrance-free products formulated for sensitive skin.
If you’re uncertain about whether you have dermatitis, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. Self-treating with over-the-counter medications can be harmful. Our Advanced Dermatology, P.C. team offers expert skin care evaluations and treatment to meet your needs.
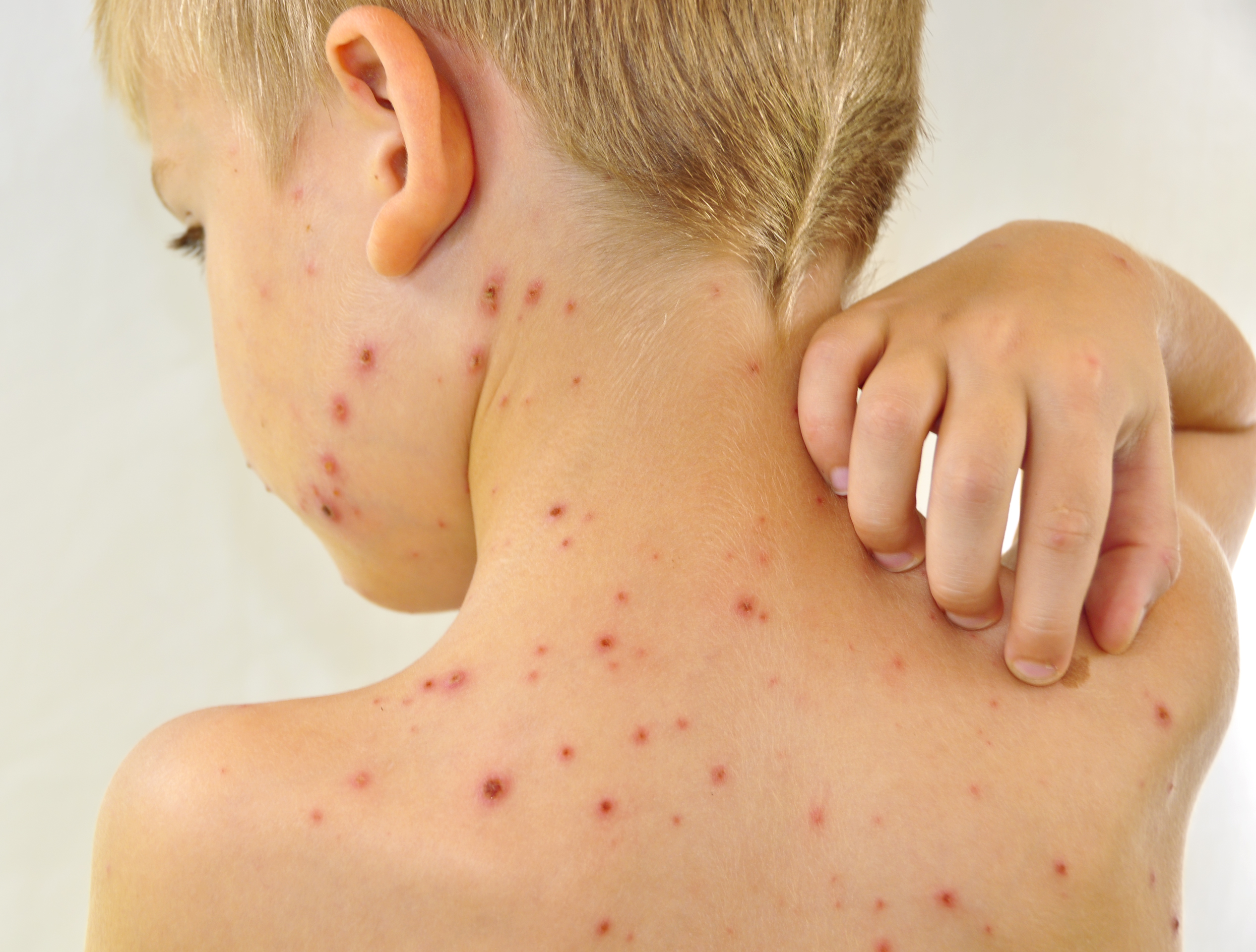
Types of eczema (dermatitis):
Atopic – A chronic skin disease directly related to the increased itching that is associated with eczema. Many times the itching becomes unbearable – enough to make normal activities difficult. It is common for the condition to form during childhood. There have been many studies that classify this specific type of dermatitis as a genetic disorder.
Contact – Once a person comes into contact with any triggers they can experience burning, itching, redness. This particular form of eczema can be hard to pinpoint because of the magnitude of things we come into contact with on a daily basis. In most cases a red rash appears (in some cases immediately, and in others it may take a few days). It takes anywhere from 3-4 weeks to clear up. If you notice the rash is not going away you should contact your dermatologist for further advice or dermatitis treatment
Dyshidrotic / Hand– Itching and burning occur in the following areas: soles of the feet, palms of the hands and sides of the fingers. Hand dermatitis many times comes because of a person’s profession, meaning the irritant or trigger can be associated with something they come in contact with at work. This is not limited to the hands only. When eczema forms on any area of the body, due to a person’s profession, it is known as occupational dermatitis.
Neurodermatitis – Is associated with something known as the “itch scratch itch cycle” This particular type of dermatitis occurs when the nerve endings in the skin become irritated. Most times the condition forms between the ages of 25-30 and for women more than men. Neurodermatitis generally results in thick leathery skin.
Nummular – Comes about when the skin has experienced a disturbance, including: an insect bite, burn, or cut. Common areas for nummular dermatitis to form are the buttocks, arms, legs and knees. Those suffering from this condition will notice coin or oval-shaped patches of dry skin in the areas listed above.
Seborrheic– Cold and dry weather are when this type of dermatitis forms the most. The common areas of formation are: the scalp (waxy/oily patches), face, cheeks, and shoulders. Common names associated with this particular type of dermatitis: dandruff, Seborrhea, or “Cradle cap” (like its name suggests it is associated with infants).
Stasis – Aging most times leads to a reduction of circulation in the lower half of the body, leading to a fluid build-up. Swelling, painful sores, skin discoloration and itchy rashes are all things that happen because of the decrease in blood flow.
Receive skincare tips, news and special offers!