Nail Infections and Disease Treatment
Fingernails and toenails protect the tissues beneath your toes and fingers. The term “nail disease” refers to various conditions affecting the nails and the skin surrounding them. Such problems may indicate anemia, lung disease, heart disease, diabetes or other medical conditions. Symptoms of nail disease include sudden changes in growth rate, discoloration, thinning or thickening, pain, bleeding, discharge, and pain. Patients experiencing nail problems should go to a dermatologist to receive proper treatment and minimize the occurrence of complications.
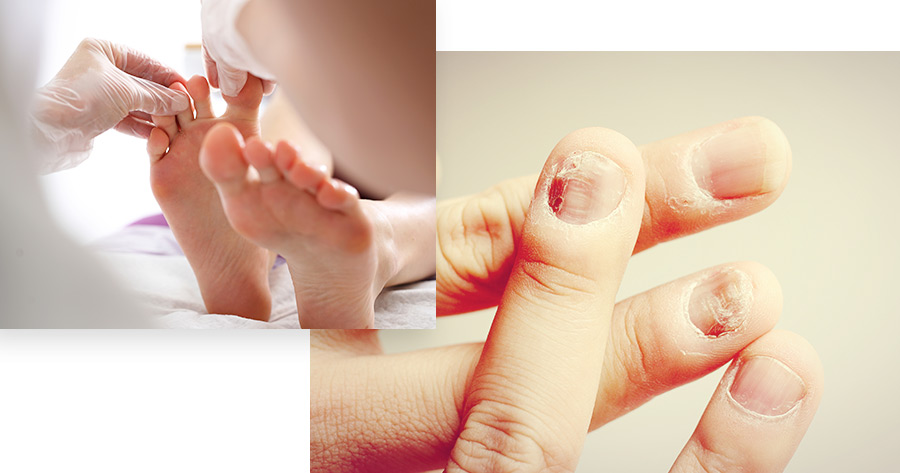
Specific Nail Conditions
Fungal Infection
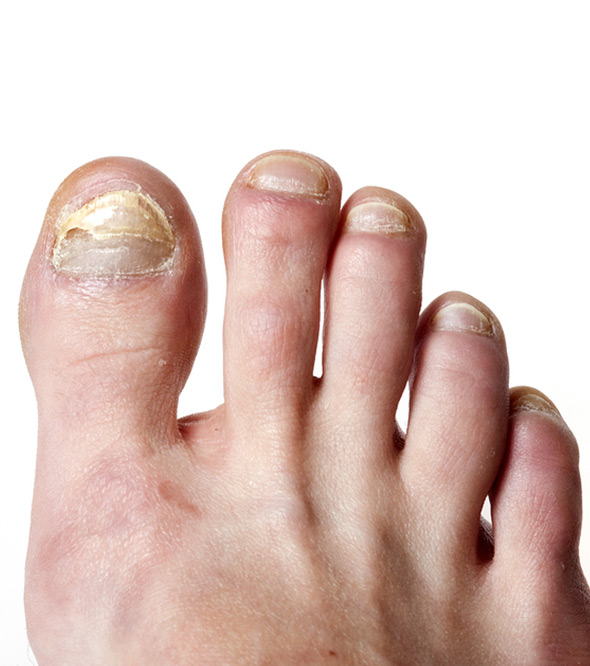
Fungal infections account for roughly 50 percent of all nail disease cases, typically affecting the toenails. The toenails may get infected in showers, locker rooms, swimming pools and other damp places in which people walk around barefoot. Symptoms of a fungal infection include discoloring and thickening of the affected toenails. If left untreated, fungal infections can spread to other toenails, the fingernails, and elsewhere throughout the skin. This can lead to walking difficulties, as infected toenails are difficult to trim and hurt when wearing shoes.
Ingrown Toenail
An ingrown toenail occurs when the side of a toenail grows into the soft tissue of that toe. This condition usually affects the big toe, although it can occur on any toe. Ingrown toenails may occur as a result of wearing cramped shoes, trauma to the feet, hereditary factors, or improperly trimming toenails. Symptoms of an ingrown toenail may include redness around the affected toenail, infection of the tissue surrounding the toenail, and swelling of the affected toe. Ingrown toenails that are left untreated may spread infection to the surrounding bone.
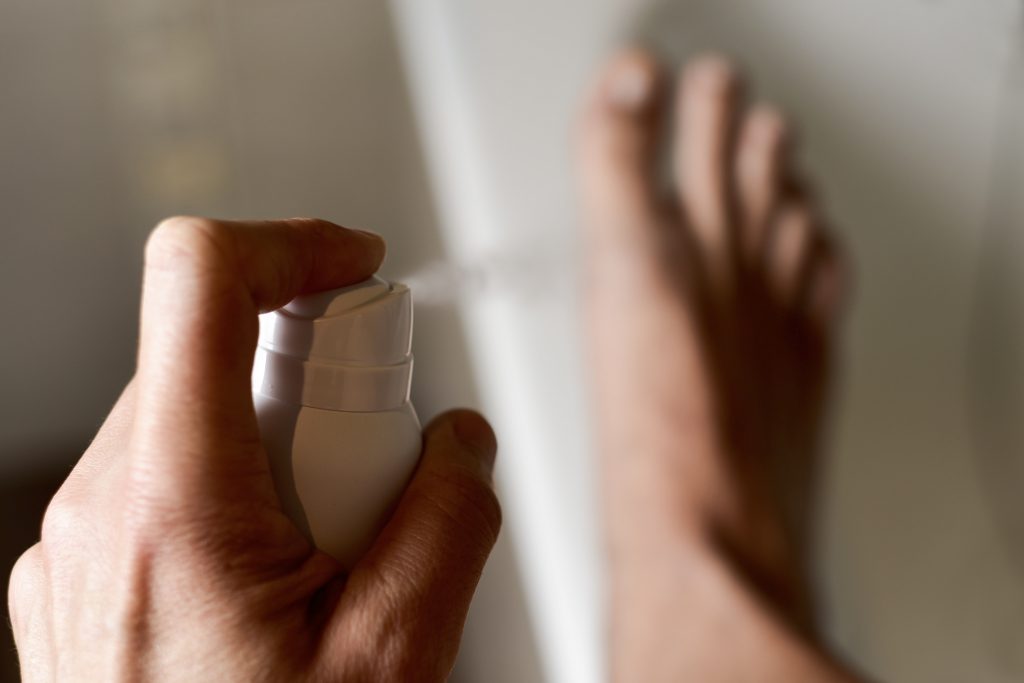
Fungal Infection
Treatment for a fungal infection varies depending on each patient’s individual condition. Mild infections may be successfully treated with over-the-counter products and daily cleansing of the affected area. Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed in certain cases. Severe fungal infections may require removal of the infected nail. Only a qualified physician can properly diagnose and treat fungal infections after a physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history.


Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails can usually be treated by regularly soaking the foot in warm water and applying antibiotic creams. More severe cases may require lifting the nail from the skin or removing part or all of the affected nail and its surrounding tissue. The exact course of treatment will vary based on each patent’s individual condition and medical history.
To know more about your condition
There are a variety of factors which can cause nail disease. To learn more about your nail condition or to schedule an appointment, contact our offices today. Our offices are conveniently located throughout New York, Queens, Long Island and New Jersey. For more information on nail disease treatment, click here.
Contact Advanced Dermatology today to schedule an appointment with Dr. Falivene.
