What is Melasma?
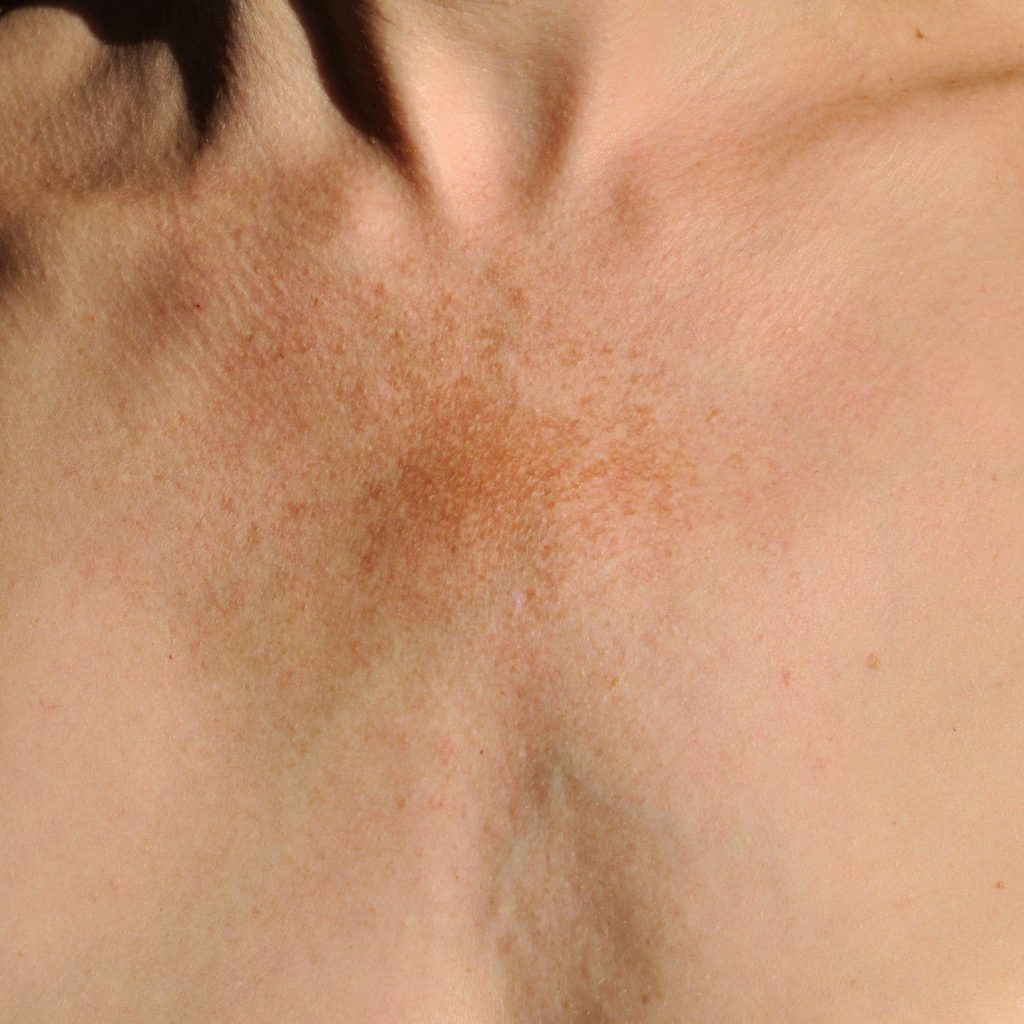
Melasma is a common skin disorder (of skin discoloration) that is often associated with sun exposure. The exact cause of Melasma is still unknown, however researchers theorize that Melasma occurs as a result of the color-making skin cells (melanocytes) producing too much color or melanin resulting in patchy discoloration. An estimated six million women in the United States have this skin condition. Those with darker skin, such as Latin/Hispanic, North African, African-American, Asian, and Indian descent are more likely to get Melasma.
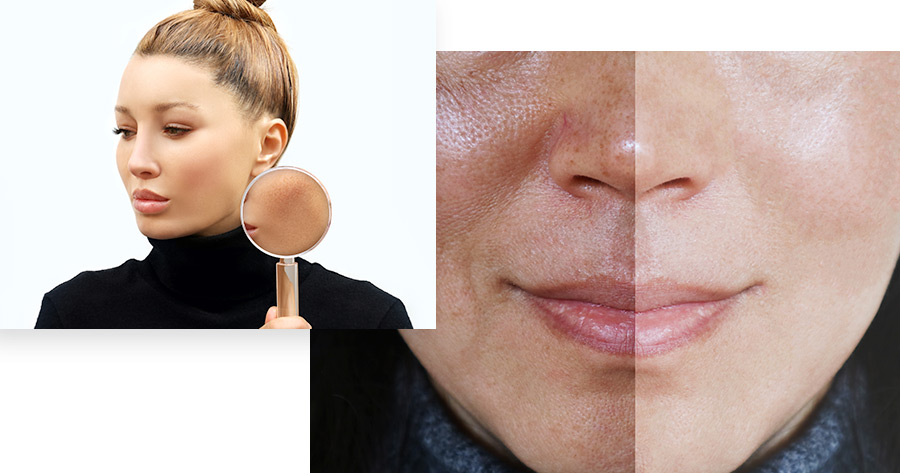

What are the probable causes of Melasma?
Triggers of Melasma include extended sun exposure, estrogen supplements, birth control pills, and pregnancy. Melasma can affect anyone, but most often it affects young women with brownish skin tone. There is also thought to be a genetic component to Melasma and those with blood relatives who had Melasma are much more likely to develop the condition.
What are the symptoms of Melasma?
Most often, Melasma presents on areas of the body that experience lots of sun exposure such as the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. However, it may also present on the neck and arms as these are areas that experience ample sun exposure as well.The symptoms of Melasma are limited to cosmetic as Melasma does not cause any sensation such as inching or burning. Often the most difficult part of Melasma is managing the psychological stress that stems from the unsightly appearance.
How is Melasma diagnosed?
In order to diagnose Melasma, our dermatologists may look at your skin under a device called a Wood’s light. In some cases, Melasma may look like another skin condition, in which case our dermatologist will perform a biopsy in which he or she would remove a small bit of skin and send it to a lab for evaluation.

Melasma can fade on its own. This often occurs when the trigger of the condition dissipates. For example, when hormone levels retract to normal levels such as after the delivery of a baby or the termination of birth control supplements. For many with Melasma, using over the counter products to treat the condition without professional advise often only results in aggravating the skin. The scrubbing and chemicals people use as household remedies usually results in darkening of the Melasma. Speak to our dermatologists before applying any products.As a means of treating Melasma, our dermatologists most often would first prescribe hydroquinone, a medicine that comes as a cream, lotion, gel, or liquid that lightens the skin.
Other products that our dermatologists may prescribe include tretinoin and corticosteroids which similarly act to lighten skin. Other topical medicines that are sometimes prescribed are azelaic acid and kojic acid that assist in lightening Melasma.If the Melasma does not respond to these medications, our dermatologists may recommend a procedure such as a chemical peel, microdermabrasion, and dermabrasion. The Fraxel laser is an alternative tool that is now used to combat Melasma. The Fraxel laser has the ability to penetrate deep into the skin and eliminate the skin cells that are producing too much pigment, thus, inhibiting the Melasma. The benefit of the Fraxel laser is that the skin’s outer layers are protected while the deeper layer of skin (dermis) with the pigment producing cells is treated. Patients that elect to have Fraxel laser therapy to treat their Melasma come to our offices periodically until the treatment regimen is complete. As mentioned above, sun avoidance is a must, before, during, and after treatment and the use of a high grade UVA and UVB sun block is of most importance.

Can I prevent Melasma?
Because sun exposure is a trigger for Melasma, dermatologists recommend avoiding sun exposure. Both UVA and UVB rays from the sun can trigger Melasma and wearing a sunscreen of SPF 30 or greater is a must. The importance of using sunscreen cannot be underestimated. In addition to helping prevent Melasma, more than 2 million people annually are diagnosed with skin cancer. Numerous studies have shown the dangerous correlation between the lack of sunscreen use and sunburns and melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. Before and after melasma treatment results further emphasize the importance of sun protection measures. We recommend everyone to apply sunscreen 20 minutes prior to going out in the sun, especially those trying to prevent Melasma or those with a history of skin cancer. In addition to sunscreen, wearing a wide-brimmed hat and extra-large sunglasses are helpful in avoiding the sun and will aide in preventing Melasma.
